Systems manager: Systems Manager: 7 Ultimate Power Roles Revealed
Ever wondered who keeps the digital backbone of a company running smoothly? Meet the systems manager—the unsung hero of modern IT operations. With tech evolving at lightning speed, this role has become more critical than ever.
What Is a Systems Manager?

A systems manager is a key IT professional responsible for overseeing the design, implementation, maintenance, and optimization of an organization’s computer systems. This includes everything from servers and networks to software applications and cloud infrastructure. Their primary goal is to ensure that all technological systems operate efficiently, securely, and in alignment with business objectives.
Core Definition and Scope
The term ‘systems manager’ can vary slightly depending on the industry or company size, but at its core, it refers to someone who manages the technical infrastructure that supports business operations. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, these professionals often work closely with network architects, cybersecurity experts, and software developers to maintain seamless system functionality.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Manages hardware, software, and network systems
- Ensures system reliability and performance
- Aligns IT infrastructure with business goals
Evolution of the Role
The role of a systems manager has evolved significantly over the past two decades. In the early 2000s, the focus was primarily on maintaining on-premise servers and internal networks. Today, with the rise of cloud computing, remote work, and AI-driven automation, systems managers must be versatile, forward-thinking, and highly adaptable.
As noted by Gartner, the modern systems manager is no longer just a technician—they are strategic leaders who influence digital transformation across departments.
“The systems manager of today is a hybrid of engineer, strategist, and change agent.” — Gartner Research, 2023
Key Responsibilities of a Systems Manager
The day-to-day duties of a systems manager are diverse and demanding. They must balance technical expertise with project management skills and business acumen. Let’s break down the most critical responsibilities.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
System Design and Implementation
One of the primary roles of a systems manager is designing and deploying IT systems that meet organizational needs. This involves evaluating current infrastructure, identifying gaps, and planning scalable solutions.
- Conducts needs assessments for new system rollouts
- Leads the integration of new technologies (e.g., ERP, CRM)
- Oversees system migration projects (on-premise to cloud)
For example, when a company decides to move to Microsoft Azure or AWS, the systems manager plays a central role in planning the architecture, ensuring data integrity, and minimizing downtime during transition.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Once systems are live, the real work begins. Regular maintenance, updates, and troubleshooting are essential to prevent outages and security breaches.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Schedules routine system updates and patches
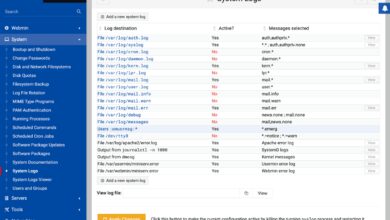
- Monitors system performance using tools like Nagios or SolarWinds
- Responds to incidents and resolves technical issues promptly
According to a 2023 IBM report, unplanned downtime costs businesses an average of $9,000 per minute. Systems managers help mitigate this risk through proactive monitoring and rapid response protocols.
Security and Compliance Management
In an era of increasing cyber threats, systems managers are on the front lines of data protection. They implement firewalls, encryption protocols, and access controls to safeguard sensitive information.
- Enforces compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA
- Conducts regular security audits and vulnerability assessments
- Develops disaster recovery and business continuity plans
They often collaborate with cybersecurity teams to ensure that all systems adhere to the latest security standards and best practices.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Essential Skills for a Systems Manager
To excel in this role, a systems manager must possess a unique blend of technical, analytical, and interpersonal skills. Let’s explore the most in-demand competencies.
Technical Proficiency
A deep understanding of IT infrastructure is non-negotiable. Systems managers must be fluent in operating systems (Windows, Linux, macOS), networking protocols (TCP/IP, DNS, DHCP), and virtualization technologies (VMware, Hyper-V).
- Expertise in cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud)
- Familiarity with scripting languages (Python, PowerShell)
- Knowledge of database management (SQL, NoSQL)
Many employers also expect certifications such as CompTIA Network+, Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator, or Cisco CCNA as proof of technical competence.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Problem-Solving and Analytical Thinking
When a server crashes or a network slows to a crawl, the systems manager must quickly diagnose the root cause and implement a solution. This requires strong analytical skills and the ability to think under pressure.
- Uses diagnostic tools to identify system bottlenecks
- Analyzes log files and performance metrics
- Applies logical reasoning to complex technical problems
Effective problem-solving often involves collaboration with other IT staff and stakeholders to gather insights and test potential fixes.
Leadership and Communication
Despite being a technical role, communication is just as important as coding or configuring routers. Systems managers frequently interact with non-technical staff, executives, and vendors.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Translates technical jargon into business-friendly language
- Leads IT teams and coordinates cross-functional projects
- Negotiates with software and hardware vendors
Strong leadership ensures that IT initiatives are understood, supported, and successfully implemented across the organization.
Systems Manager vs. IT Manager: What’s the Difference?
While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there are distinct differences between a systems manager and an IT manager. Understanding these distinctions can help clarify career paths and organizational roles.
Scope of Responsibility
A systems manager typically focuses on the technical aspects of IT infrastructure—servers, networks, databases, and system performance. Their expertise lies in the ‘how’ of technology.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
In contrast, an IT manager has a broader scope, overseeing the entire IT department, including budgeting, staffing, vendor management, and strategic planning. They are more concerned with the ‘why’ and ‘what’ of technology use.
“Think of the systems manager as the architect of the engine, while the IT manager is the driver of the car.”
Career Progression
Many systems managers eventually move into IT management roles as they gain experience and leadership skills. This progression is natural, as hands-on technical knowledge provides a solid foundation for strategic decision-making.
- Entry-level: Systems Administrator
- Mid-level: Systems Manager
- Senior-level: IT Manager or Director of IT
Some professionals choose to specialize further, becoming cloud infrastructure managers or cybersecurity operations leads instead of moving into general management.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Tools and Technologies Used by Systems Managers
The effectiveness of a systems manager heavily depends on the tools they use. From monitoring software to automation platforms, these technologies enable them to manage complex environments efficiently.
Monitoring and Management Platforms
Real-time visibility into system health is crucial. Tools like SolarWinds, Nagios, and Datadog allow systems managers to track server performance, network traffic, and application uptime.
- Alerts for CPU spikes, memory leaks, or disk failures
- Dashboard views for quick status checks
- Historical data for trend analysis
These platforms help prevent issues before they escalate into major outages.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Automation and Scripting Tools
Manual configuration of hundreds of servers is no longer feasible. Automation tools like Ansible, Puppet, and Chef enable systems managers to deploy, configure, and update systems at scale.
- Automates repetitive tasks (e.g., user provisioning)
- Ensures consistency across environments
- Reduces human error and saves time
For example, Ansible allows a systems manager to push a configuration change to 100 servers with a single command, drastically improving efficiency.
Cloud and Virtualization Technologies
With over 90% of enterprises now using cloud services, systems managers must be proficient in platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Manages virtual machines and containers (Docker, Kubernetes)
- Configures cloud storage and backup solutions
- Optimizes cloud costs through resource tagging and auto-scaling
According to Synergy Research Group, global cloud infrastructure spending reached $250 billion in 2023, underscoring the importance of cloud expertise for systems managers.
How to Become a Systems Manager
Becoming a systems manager typically requires a combination of education, certifications, and hands-on experience. Here’s a roadmap to help you get started.
Educational Background
Most systems managers hold at least a bachelor’s degree in computer science, information technology, or a related field. Coursework in networking, operating systems, and database management provides a strong foundation.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Common degrees: B.S. in Computer Science, IT, or Engineering
- Some employers prefer candidates with a master’s degree in IT management
- Bootcamps and online courses (e.g., Coursera, edX) can supplement formal education
However, many successful systems managers are self-taught or have transitioned from other IT roles through experience and certification.
Key Certifications
Certifications validate technical skills and can significantly boost employability. Some of the most respected credentials include:
- CompTIA A+ and Network+: Foundational IT knowledge
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator Associate: Cloud management
- Cisco CCNA: Networking expertise
- Red Hat Certified Engineer (RHCE): Linux system administration
- ITIL Foundation: Best practices in IT service management
Many professionals pursue these certifications while working in entry-level IT roles like help desk technician or systems administrator.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Gaining Practical Experience
Real-world experience is invaluable. Starting in roles such as IT support, network technician, or junior systems administrator allows aspiring systems managers to build technical skills and understand organizational workflows.
- Work on system upgrades, patch deployments, and user support
- Participate in disaster recovery drills
- Volunteer for cross-departmental IT projects
Over time, this experience builds the confidence and competence needed to take on managerial responsibilities.
The Future of the Systems Manager Role
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the role of the systems manager. Emerging trends like artificial intelligence, edge computing, and zero-trust security are reshaping expectations and responsibilities.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Impact of AI and Automation
AI-powered tools are beginning to automate routine monitoring and troubleshooting tasks. For example, machine learning algorithms can predict disk failures or detect anomalous network behavior before humans notice.
Instead of replacing systems managers, AI is augmenting their capabilities. The future systems manager will spend less time on manual fixes and more time on strategic planning, optimization, and innovation.
“AI won’t replace systems managers, but systems managers who use AI will replace those who don’t.” — TechCrunch, 2024
Rise of Hybrid and Edge Computing
With more companies adopting hybrid cloud models (mix of on-premise and cloud), systems managers must become experts in managing distributed environments.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Ensure seamless integration between local and cloud systems
- Manage latency and bandwidth issues in edge computing setups
- Implement consistent security policies across all locations
This shift requires a deeper understanding of network architecture and data flow optimization.
Increased Focus on Cybersecurity
As cyberattacks grow in frequency and sophistication, systems managers are expected to play a larger role in proactive defense. This includes implementing zero-trust frameworks, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring.
- Collaborate with CISOs and security analysts
- Conduct regular penetration testing and risk assessments
- Stay updated on emerging threats and mitigation strategies
The systems manager of the future will be a key player in an organization’s overall security posture.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
What does a systems manager do?
A systems manager oversees the design, implementation, maintenance, and security of an organization’s IT infrastructure. They ensure that computer systems, networks, and software operate efficiently and align with business goals. Their responsibilities include troubleshooting, performance monitoring, and leading technology upgrades.
How much does a systems manager earn?
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for computer and information systems managers was $164,000 in 2023. Salaries can vary based on location, industry, and experience, with top earners in tech hubs like San Francisco or New York making over $200,000.
Is a degree required to become a systems manager?
While many employers prefer a bachelor’s degree in computer science or IT, it’s not always mandatory. Some professionals enter the field through certifications, bootcamps, and hands-on experience. However, a degree can accelerate career advancement and open doors to higher-level positions.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
What certifications are best for a systems manager?
Top certifications include Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator, Cisco CCNA, CompTIA Network+, Red Hat RHCE, and ITIL Foundation. Cloud and security certifications are increasingly valuable as organizations adopt hybrid environments and face growing cyber threats.
What’s the difference between a systems administrator and a systems manager?
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
A systems administrator focuses on day-to-day operations like user support and system updates, while a systems manager has a broader role that includes strategic planning, team leadership, and project management. The manager often supervises administrators and makes high-level infrastructure decisions.
The role of a systems manager is more vital than ever in our digital-first world. From ensuring system reliability to driving innovation, they are the backbone of modern IT operations. As technology evolves, so too must the skills and strategies of these professionals. Whether you’re aspiring to become one or looking to hire a top-tier systems manager, understanding their responsibilities, tools, and future trajectory is essential for success in the tech-driven landscape.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Further Reading: